Whiplash is a common injury that occurs in rear-end collisions, but not many people truly understand what it is or how it happens. It’s important to have a thorough understanding of this injury, as it can lead to long-term pain and discomfort if not treated properly. In this article, we will dive into the details of whiplash and its causes, specifically in the context of rear-end collisions.
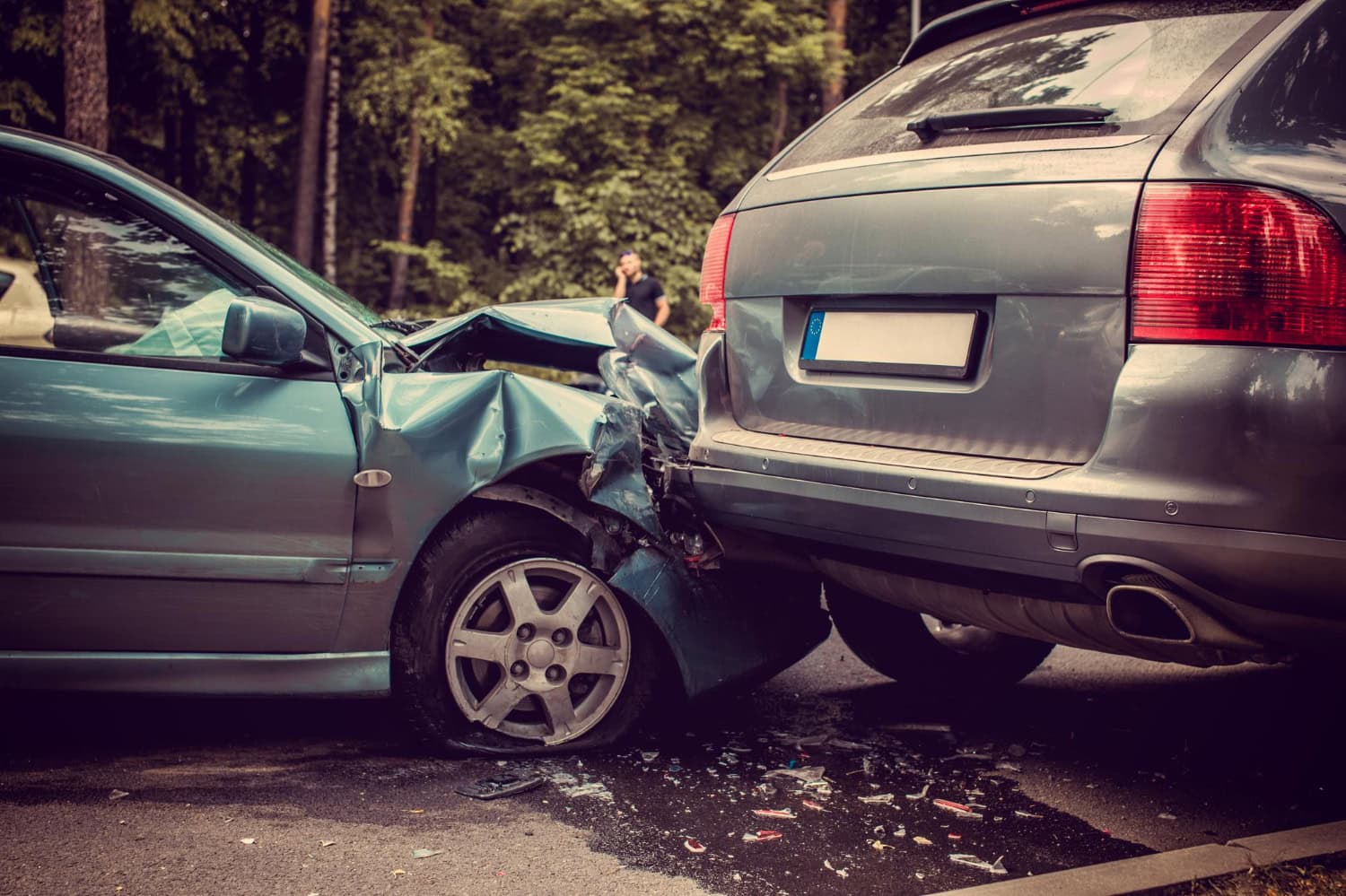
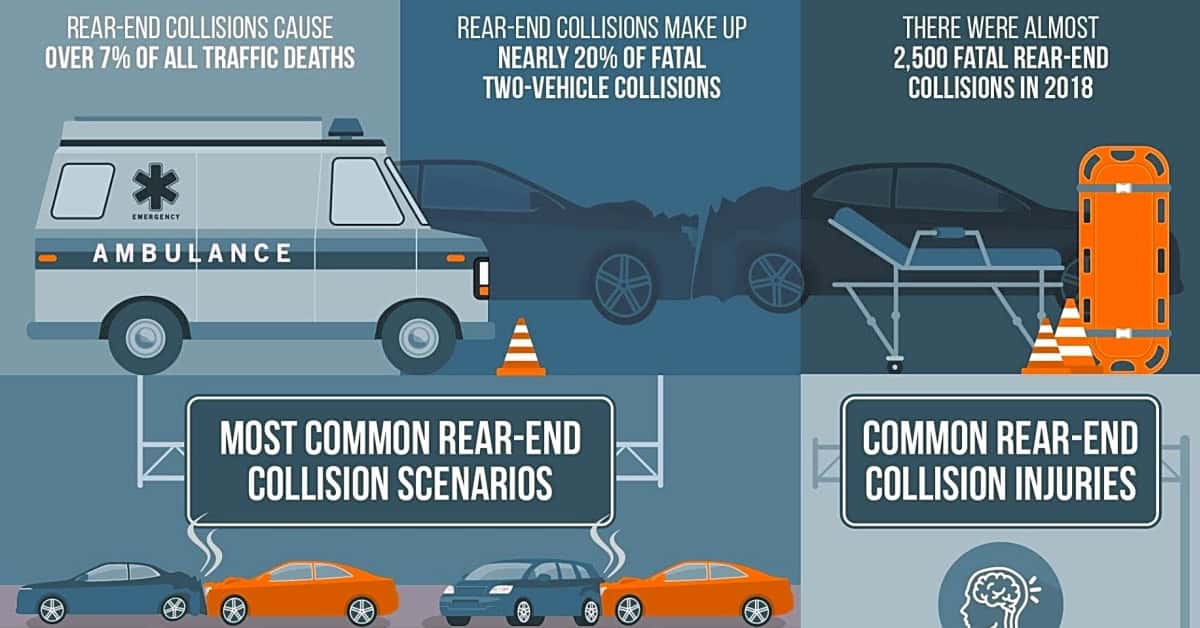
Rear-end collisions are a frequent occurrence on the roads, and they can happen to anyone. Whether you’re driving in heavy traffic or cruising on the highway, a rear-end collision can happen in the blink of an eye. And unfortunately, these types of accidents are one of the leading causes of whiplash injuries.
But what exactly is whiplash? How does it happen? And why is it such a common injury in rear-end collisions? These are just some of the questions we will answer in this article. By the end, you will have a better understanding of this often misunderstood injury and be better equipped to handle it if you find yourself in a rear-end collision.
Firstly, it’s important to understand that a rear-end collision occurs when one vehicle crashes into the back of another vehicle. This often happens due to following too closely, distracted driving, or sudden stops. As a result, the impact from the collision can cause a sudden and forceful movement of the head and neck, leading to whiplash injuries.
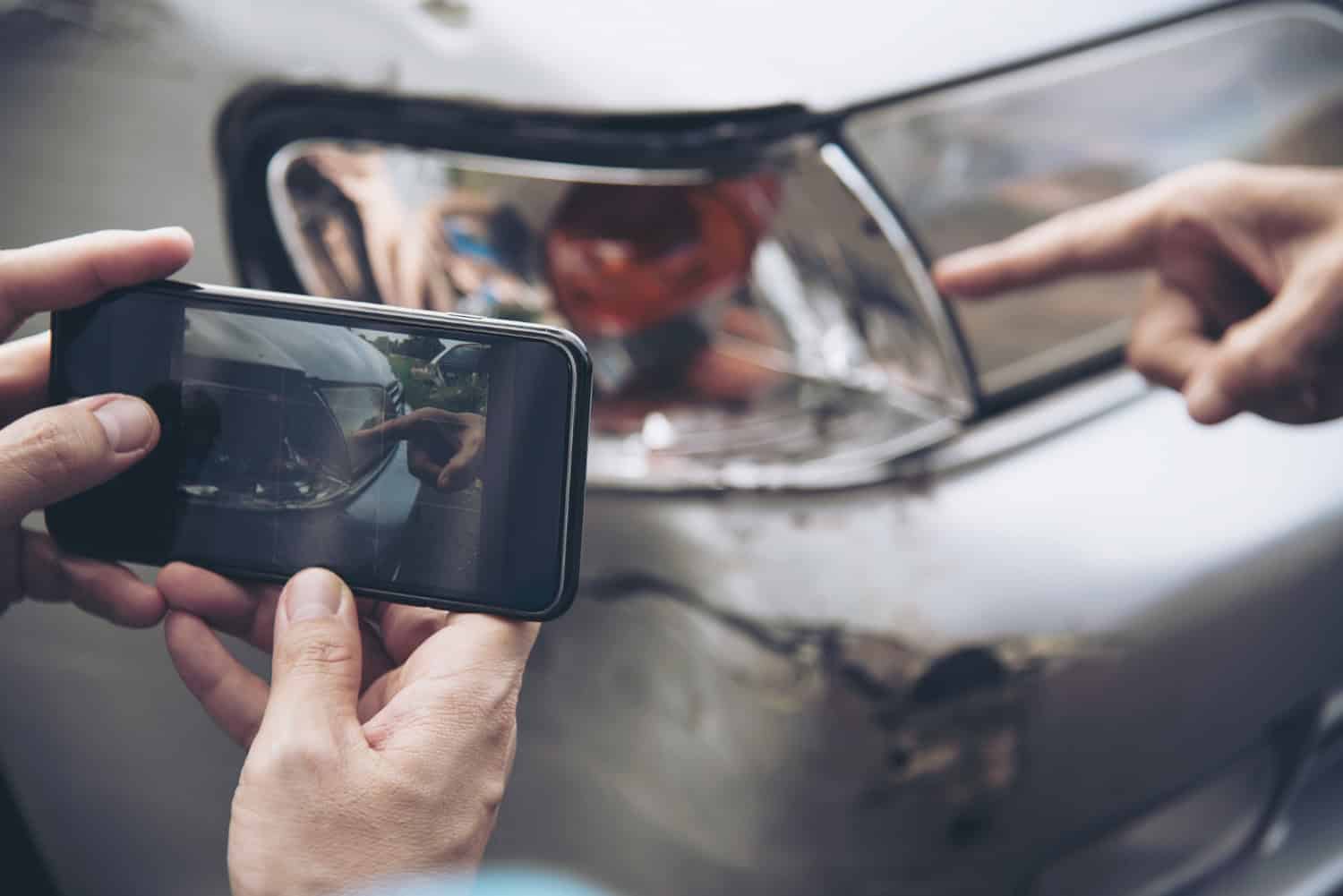
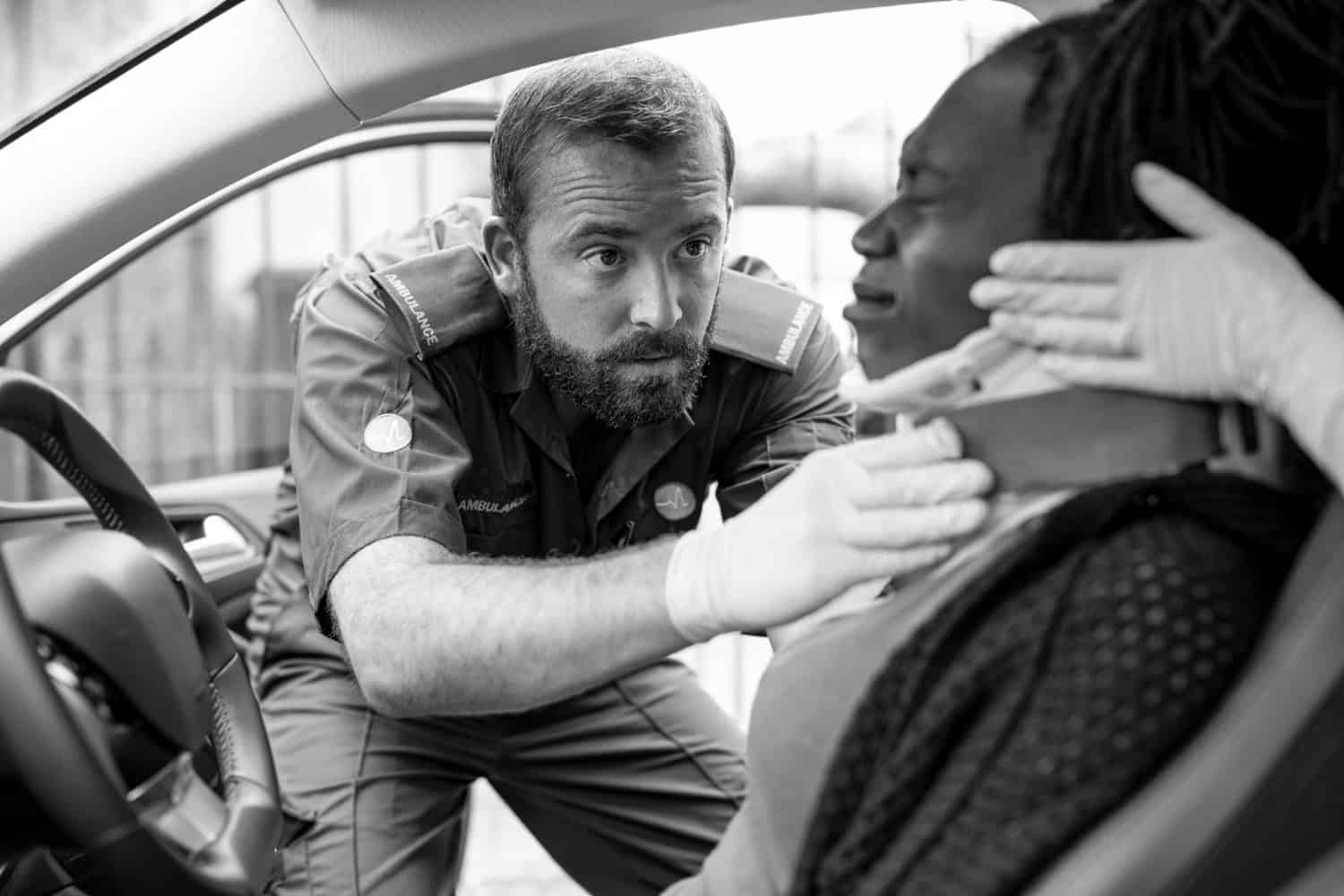
To better understand the causes of rear-end collisions, it’s important to know what to do after being involved in one. This may include information on contacting your insurance company, seeking compensation for damages or injuries, and understanding your legal rights. It’s also crucial to seek medical attention immediately, even if you don’t feel injured at the time of the accident. Whiplash symptoms can take several days to appear, and early treatment can prevent further complications.
In terms of insurance coverage, it’s important to have proper coverage for accidents like rear-end collisions. This may include liability coverage, which covers damages to the other driver’s vehicle and any injuries they sustain. Additionally, having personal injury protection (PIP) or medical payments coverage can help cover your own medical expenses.
Moving on to the main focus of this article, let’s delve into the topic of whiplash injuries. Whiplash is a common injury that occurs in rear-end collisions, where the sudden movement of the head and neck can cause damage to the soft tissues and muscles. Symptoms of whiplash may include neck pain, stiffness, headaches, dizziness, and difficulty sleeping. It’s important to seek medical treatment for whiplash, as it can lead to long-term complications if left untreated.
To prevent rear-end collisions and the resulting injuries like whiplash, it’s important to always practice safe driving habits. This includes maintaining a safe distance from other vehicles, avoiding distractions while driving, and being prepared for sudden stops. Additionally, regular car maintenance can help prevent accidents due to vehicle malfunctions.
In conclusion, being involved in a rear-end collision can be a frightening and overwhelming experience. However, understanding the causes of these accidents and their potential injuries, such as whiplash, can help you better prepare for and handle such situations. By following proper safety measures and seeking prompt medical attention, you can minimize the risks and consequences of rear-end collisions.
What to Do After a Rear-End Collision
After being involved in a rear-end collision, it’s important to take certain steps to ensure your safety and protect your well-being. Here are the two most crucial things you should do immediately following the accident:
- Contact Your Insurance Provider – Whether you were at fault or not, it’s important to contact your insurance company as soon as possible after the accident. They will be able to guide you through the process of filing a claim and getting the compensation you need for any damages.
- Seek Medical Attention – Even if you feel fine after the accident, it’s always a good idea to get checked out by a medical professional. Whiplash and other injuries may not show symptoms right away, and seeking medical attention can help prevent any potential long-term effects.
Following these two steps can help ensure that you are properly taken care of and can begin the road to recovery after a rear-end collision. Remember to always prioritize your safety and well-being in these situations.
Understanding Whiplash Injuries
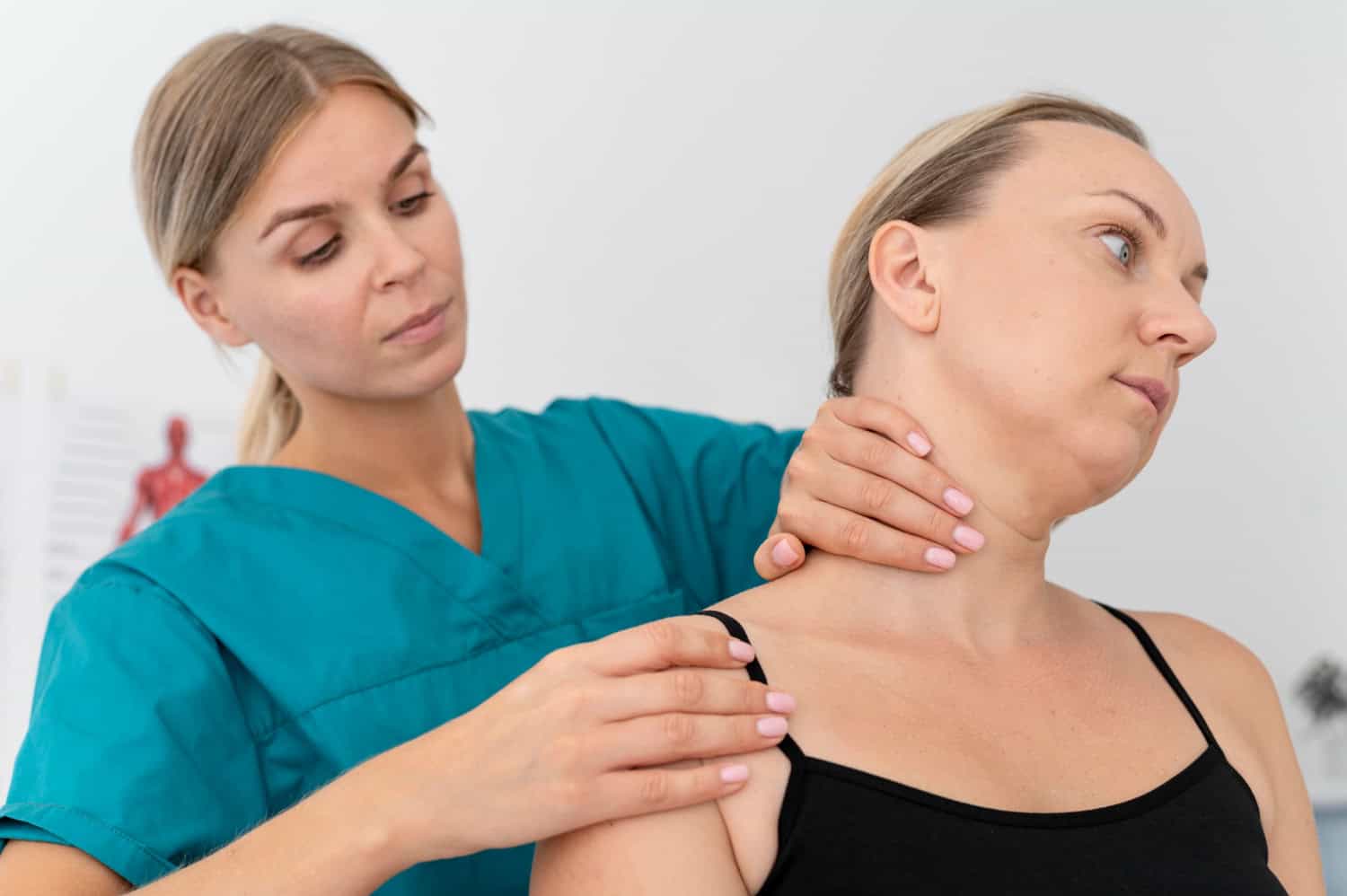
Whiplash is a common injury that occurs in rear-end collisions. It happens when there is a sudden jerking of the head, causing strain and damage to the neck. This injury can have a lasting impact on a person’s health and well-being, making it important to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes of Whiplash: The main cause of whiplash is the sudden impact of a rear-end collision. This can happen at any speed and can even occur in low-impact accidents. The force of the impact can cause the neck to move back and forth quickly, resulting in strain on the muscles and ligaments in the neck.
Symptoms of Whiplash: The symptoms of whiplash may not be immediately apparent after a rear-end collision. It can take hours or even days for symptoms to appear. Some common symptoms of whiplash include neck pain and stiffness, headaches, dizziness, and difficulty moving the neck.
Treatment Options for Whiplash: If you are experiencing symptoms of whiplash after a rear-end collision, it’s important to seek medical attention. Treatment options may include rest, pain medication, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery. It’s crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions and attend all necessary appointments to ensure a full recovery.
Tips for Preventing Rear-End Collisions
Rear-end collisions are a common type of car accident that can cause serious injuries, such as whiplash. However, these accidents can be prevented by practicing safe driving habits and regular car maintenance. By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of being involved in a rear-end collision.
1. Keep a safe distance from the car in front of you
One of the main causes of rear-end collisions is following too closely behind the car in front of you. This doesn’t give you enough time to react if the car suddenly brakes or slows down. To prevent this, make sure to keep a safe distance between your car and the one in front of you. The general rule is to stay at least three seconds behind the car in front of you.
2. Pay attention to the road and other drivers
Distracted driving is another common cause of rear-end collisions. Avoid texting, eating, or doing anything else that takes your attention away from the road while driving. Also, be aware of other drivers around you and anticipate their actions. If you see a car braking suddenly, be prepared to do the same.
3. Maintain your car’s brakes and tires
Regular car maintenance is essential for preventing rear-end collisions. Make sure to get your brakes and tires checked regularly to ensure they are in good condition. Worn out brakes or bald tires can increase your risk of being involved in an accident.
4. Use your turn signals
Using your turn signals not only helps other drivers anticipate your actions, but it also helps prevent rear-end collisions. By signaling when you are changing lanes or turning, you give other drivers time to react and avoid colliding with your car.
5. Adjust your driving for weather conditions
Bad weather can make roads slippery and decrease visibility, increasing the risk of rear-end collisions. Make sure to adjust your driving accordingly by slowing down and leaving more space between your car and others. Also, make sure to turn on your headlights in low visibility conditions.
By understanding the causes of rear-end collisions and their potential injuries like whiplash, you can better protect yourself on the road. Remember to always practice safe driving habits and seek medical attention if you are involved in an accident.